Procter & Gamble Co.: A Deep Dive into a Consumer Staples Giant
Navigating Market Dynamics, Financial Health, and Future Prospects in the Ever-Evolving Consumer Landscape
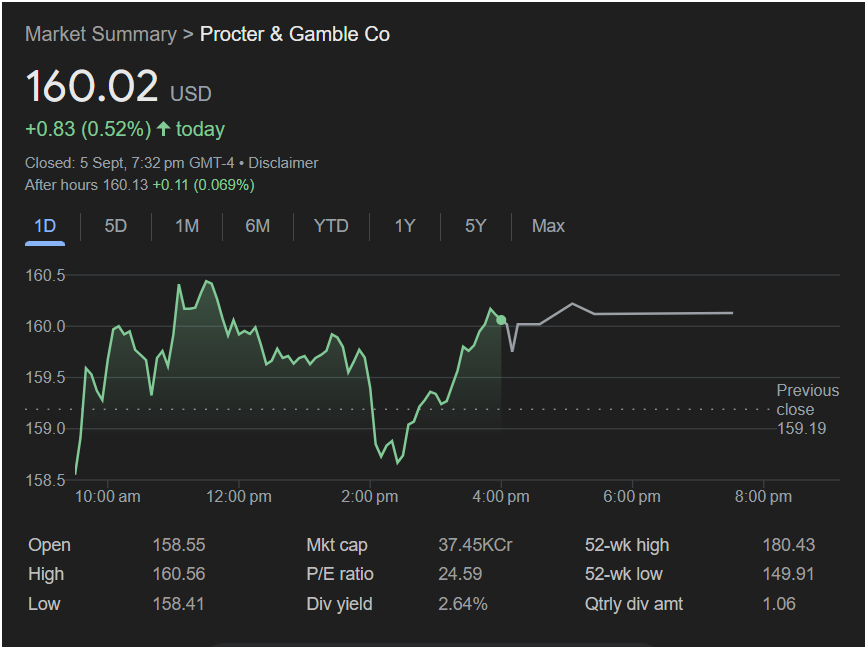
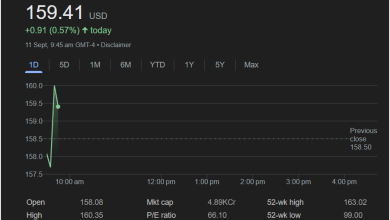
Procter & Gamble Co. (P&G) stands as an undisputed titan in the consumer goods industry, a conglomerate whose myriad brands touch billions of lives daily across the globe. From the moment one brushes their teeth with Crest, washes their hair with Head & Shoulders, cleans their clothes with Tide, or comforts a baby with Pampers, P&G’s presence is almost inescapable. This pervasive influence is not merely a testament to its marketing prowess but a reflection of its historical endurance, strategic brand management, and relentless pursuit of consumer insights. The market summary provided offers a snapshot of its recent stock performance, trading at 160.02 USD, reflecting a modest daily gain. This single data point, however, is merely the tip of an expansive iceberg when attempting to understand the complexities and nuances of a company of P&G’s stature.
Historical Context and Brand Portfolio:
To truly appreciate P&G’s current standing, one must first acknowledge its deeply entrenched history. Founded in 1837 by William Procter and James Gamble in Cincinnati, Ohio, the company began as a small soap and candle business. Over nearly two centuries, it has evolved into a multinational corporation with one of the most extensive and diverse portfolios of household and personal care products. This evolution has been characterized by strategic acquisitions, divestitures, and continuous innovation. Think of iconic brands like Gillette in male grooming, Bounty in paper products, Dawn in dishwashing, or Charmin in toilet paper – each represents a category leader, meticulously nurtured and grown under the P&G umbrella.
The sheer breadth of its brand portfolio is both a strength and a challenge. On one hand, it provides significant diversification, insulating the company from downturns in any single category or product line. If sales of beauty products falter, home care might pick up the slack. On the other hand, managing such a vast array of brands requires immense organizational efficiency, sophisticated supply chain management, and a deep understanding of varied consumer needs and cultural preferences across different geographies. The strategic decision a few years ago to streamline its portfolio, divesting numerous non-core brands to focus on its most profitable and high-growth segments, was a clear indication of this ongoing strategic refinement. This move aimed to unlock greater agility and resource allocation towards brands with stronger competitive advantages and higher margins, emphasizing quality over sheer quantity of brands.
Market Performance and Valuation Metrics:
The provided market summary highlights several key financial metrics crucial for investors and analysts. The stock’s current price of 160.02 USD, with a slight daily increase, reflects ongoing market activity. The “52-wk high” of 180.43 and “52-wk low” of 149.91 illustrate the volatility and range within which P&G’s stock has traded over the past year. Understanding these bounds is vital for assessing investor sentiment and potential entry or exit points for stock. A stock trading closer to its 52-week high might suggest strong recent performance and positive outlook, while being closer to its 52-week low could indicate recent challenges or undervaluation.
The “Mkt cap” (Market capitalization) of 37.45KCr (likely referring to Trillion, given the scale of P&G, perhaps 374.5 Billion USD if ‘Cr’ implies ‘Crore’ in a different context or a typo) is a critical indicator of the company’s size and overall market value. A company of P&G’s market cap signifies its status as a large-cap stock, often considered more stable and less prone to extreme fluctuations compared to smaller companies. This stability is often attractive to institutional investors and those seeking long-term, relatively secure investments.
The “P/E ratio” (Price-to-Earnings ratio) stands at 24.59. This metric is a fundamental valuation tool, indicating how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of P&G’s earnings. A P/E ratio of 24.59 suggests that investors are expecting future earnings growth, or they value P&G’s stability and consistent dividends highly. Comparing this P/E to industry averages, historical P&G P/Es, and competitor P/Es (like Unilever, Colgate-Palmolive, or Kimberly-Clark) is crucial for a complete valuation perspective. A higher P/E could imply that the stock is relatively expensive, while a lower one might suggest it’s undervalued, though these are never absolute indicators without broader context.
The “Div yield” (Dividend yield) of 2.64% and “Qtrly div amt” (Quarterly dividend amount) of 1.06 USD are particularly important for income-focused investors. P&G is renowned for its consistent dividend payments and its status as a “Dividend Aristocrat” or “Dividend King,” having increased its dividends for decades. This track record is a strong signal of financial health, consistent cash flow generation, and a commitment to returning value to shareholders. For many investors, especially retirees or those building a passive income stream, P&G’s dividend reliability is a core component of its investment appeal, providing a tangible return regardless of short-term stock price fluctuations.
Operational Efficiency and Supply Chain:
Operating a global enterprise of P&G’s scale demands extraordinary operational efficiency and a robust supply chain. Manufacturing, sourcing raw materials, distributing products to millions of retail outlets, and managing inventory across diverse geographies are monumental tasks. The COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent global supply chain disruptions have highlighted the critical importance of resilience and adaptability in these areas. P&G, like many large corporations, has likely invested heavily in optimizing its logistics, leveraging technology for forecasting and inventory management, and diversifying its supplier base to mitigate risks.
Furthermore, efficiency extends beyond the physical movement of goods to internal processes, research and development (R&D), and marketing spend. P&G’s significant R&D investments are crucial for product innovation, which is the lifeblood of the consumer goods industry. Developing new formulations, improving product efficacy, and creating sustainable packaging solutions are all outcomes of a well-funded and strategic R&D function. The ability to bring these innovations to market effectively, supported by impactful marketing campaigns, directly translates into sales growth and market share gains.
Competitive Landscape and Market Challenges:
The consumer goods market is intensely competitive, characterized by established rivals, emerging direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands, and the ever-present threat of private label products from retailers. P&G competes fiercely with companies like Unilever, Kimberly-Clark, Colgate-Palmolive, and Reckitt Benckiser, among others. This competition plays out in terms of product quality, pricing, innovation, and shelf space in retail environments.
Several macro trends pose ongoing challenges for P&G:
-
Evolving Consumer Preferences: Consumers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, ethical sourcing, natural ingredients, and personalized experiences. Brands that fail to adapt to these shifting values risk losing relevance. P&G has responded by investing in sustainable packaging, launching “cleaner” product lines, and increasing transparency about its supply chain practices.
-
Digital Disruption and E-commerce: The rise of e-commerce has fundamentally altered how consumers shop. While traditional retail remains crucial, online sales channels, including P&G’s own brand websites and partnerships with major online retailers, are growing in importance. This shift requires different marketing strategies, logistics capabilities, and a deeper understanding of digital consumer journeys. The proliferation of social media also means that brand reputation can be built or damaged rapidly through online discourse.
-
Inflationary Pressures and Cost Management: Rising costs for raw materials, energy, and labor can significantly impact P&G’s profitability. The company’s ability to manage these costs through efficiency gains, strategic sourcing, and judicious pricing adjustments is critical. However, passing on price increases to consumers must be carefully balanced to avoid alienating customers, especially in highly price-sensitive categories.
-
Geopolitical and Economic Volatility: Global events, from regional conflicts to economic recessions, can disrupt supply chains, impact consumer spending power, and create currency fluctuations that affect P&G’s international earnings. Operating in nearly every country in the world means P&G is inherently exposed to these global dynamics, requiring sophisticated risk management strategies.
-
Rise of Private Labels and Discount Brands: Retailers are increasingly developing their own private label brands, which often offer similar quality at lower prices, putting pressure on established brand-name products. Additionally, discount brands continue to attract cost-conscious consumers, forcing P&G to constantly justify the premium its brands command through perceived value, innovation, and brand loyalty.
Innovation and Sustainability:
Innovation is not a luxury but a necessity for P&G. It fuels product differentiation, allows for premium pricing, and creates new market opportunities. P&G’s innovation strategy encompasses not only groundbreaking new products but also continuous improvement of existing ones, focusing on efficacy, convenience, and increasingly, sustainability.
Sustainability, in particular, has moved from a niche concern to a core business imperative. Consumers, regulators, and investors are all demanding greater environmental and social responsibility. P&G’s initiatives in this area might include:
-
Sustainable Packaging: Reducing plastic use, increasing recycled content, and exploring refillable packaging solutions.
-
Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving technologies in manufacturing and developing products that require less water for use.
-
Renewable Energy: Shifting towards renewable energy sources for its operations.
-
Ethical Sourcing: Ensuring that raw materials are sourced responsibly and ethically, without contributing to deforestation or unfair labor practices.
These initiatives are not just about corporate social responsibility; they are increasingly seen as drivers of competitive advantage, enhancing brand reputation, attracting environmentally conscious consumers, and potentially leading to cost savings in the long run.
The Role of Consumer Insights and Marketing:
P&G’s enduring success is intrinsically linked to its unparalleled ability to understand and connect with consumers. Its marketing and consumer insight capabilities are among the best in the world. This involves extensive market research, behavioral analysis, and the adept use of advertising across various media channels. From traditional television commercials to sophisticated digital campaigns, P&G consistently invests heavily in building and maintaining brand awareness and loyalty.
The digital age has brought new challenges and opportunities for consumer engagement. Data analytics now plays a crucial role in understanding consumer behavior, personalizing marketing messages, and optimizing advertising spend. P&G’s ability to harness big data to identify emerging trends, segment audiences, and tailor product offerings will be key to its continued relevance. The shift from mass marketing to more targeted and personalized communication is an ongoing evolution that P&G must master.
Future Outlook and Open Questions:
As P&G navigates the future, several open-ended questions remain pertinent:
-
How will P&G continue to balance premium pricing with increasing consumer sensitivity to cost, especially in inflationary environments? Will it need to introduce more value-tier offerings, or will its brand strength allow it to maintain its premium positioning?
-
What will be the next major wave of innovation in consumer goods, and how quickly can P&G capitalize on it? Will it be in biotechnology-driven ingredients, hyper-personalized products, or entirely new categories driven by smart home integration?
-
Can P&G successfully integrate advanced technologies like AI and machine learning across its operations, from supply chain optimization to personalized marketing, to maintain its competitive edge?
-
How will the company adapt to changing retail landscapes, particularly the continued growth of e-commerce and direct-to-consumer models? Will it continue to rely on traditional retail partnerships, or will it aggressively build out its own online channels and subscription services?
-
What impact will increasing regulatory scrutiny on environmental claims, ingredient transparency, and advertising practices have on P&G’s business model and brand communication?
-
As global demographics shift, particularly with aging populations in some regions and growing middle classes in others, how will P&G tailor its product portfolio and marketing strategies to meet these diverse needs?
-
How will P&G respond to the ongoing fragmentation of media consumption and the rise of influencer marketing and community-driven commerce? Will its historically effective large-scale advertising models remain as potent, or will it need to fundamentally rethink its approach to brand building?
Procter & Gamble’s journey is a continuous narrative of adaptation, innovation, and strategic evolution. Its strong financial position, robust brand portfolio, and global reach provide a solid foundation. However, the dynamic nature of the consumer goods market, driven by rapidly changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and macroeconomic shifts, ensures that P&G’s story will always be one of ongoing transformation, without a definitive endpoint. The stock price, the P/E ratio, and the dividend yield are mere markers along this enduring and complex trajectory, each offering a glimpse into the multifaceted life of a true corporate giant. Its future chapters will undoubtedly be as fascinating and challenging as its past.